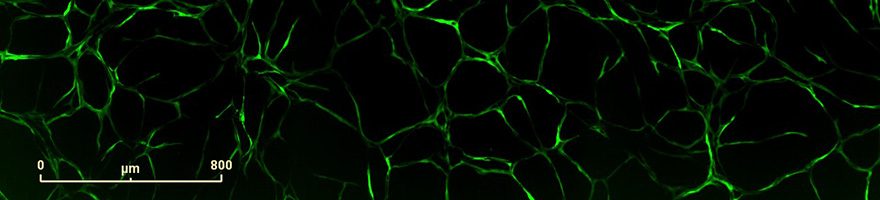
The ADSC/ECFC model yields rapidly forming (<48h) endothelial cell‘cord’structures. In the NHDF/HUVEC slowly forming‘tube-like’structures appear which continue to develop and branch even after 10days in culture. High basal formation was observed in the ADSC/ECFC model, but not in the NHDF/HUVEC model. From immuno-cytochemistry, the ADSCs surrounding the cord network label for PDGFR-β and a-SMA, suggesting apericyte phenotype.The pharmacological effects of growth factors and different pathway inhibitors were largely comparable. Interestingly, established cords and tubes display marked resistance to Avastin (Bevacizumab) compared to developing networks. G-secretase inhibition partially reversed established tubes in ADSC/ECFCs and augmented late state branching in the NHDF/HUVEC model. We conclude that these 2 models exhibit strikingly different morphological, temporal and pharmacological profiles. The resistance of established vascular structures to disruption by Avastin (Bevazicumab) may represent a useful translational paradigm for addressing tumour resistance of anti-VEGF therapies.
Read more